Macro (Vision)
It’s very important to reuse test code. You can register routine work as macro.
Creating macro object/function
- Create an object class in any place under
src/test/kotlin. For example, createmacropackage directory, then createMacroObject1.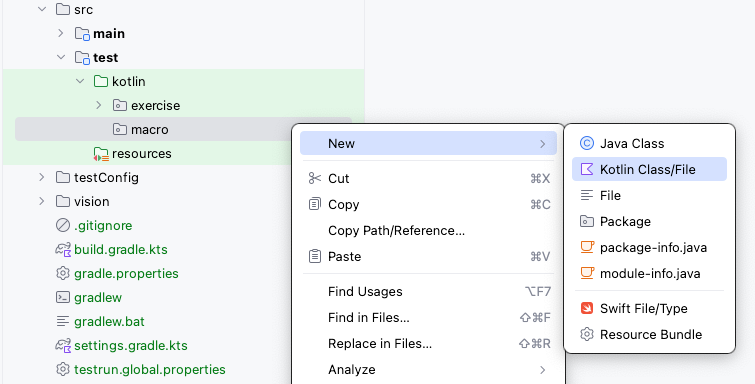

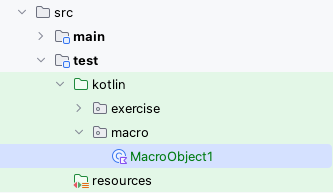
- Implement code as follows.
- Put @MacroObject annotation on the object class.
- Inherit from TestDrive interface.
- Create a function and put @Macro annotation on it.
package macro
import shirates.core.macro.Macro
import shirates.core.macro.MacroObject
import shirates.core.vision.driver.commandextension.tap
import shirates.core.vision.driver.commandextension.waitScreen
import shirates.core.vision.testcode.VisionTest
@MacroObject
object MacroObject1 : VisionTest() {
@Macro("[Network preferences Screen]")
fun internetScreen() {
it.waitScreen("[Android Settings Top Screen]")
.tap("Network & internet")
it.waitScreen("[Network & internet Screen]")
.tap("Internet")
it.waitScreen("[Internet Screen]")
.tap("Network preferences")
}
}
- Build the project. The class file of the macro is output in
builddirectory.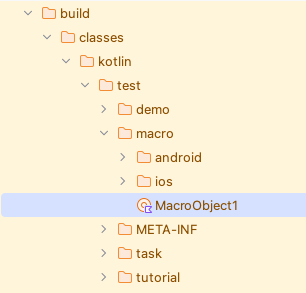
Calling macro function
- Create class
Macro1underkotlin/exercise. - Implement test code as follows.
package exercise
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Order
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test
import shirates.core.vision.driver.commandextension.exist
import shirates.core.vision.driver.commandextension.macro
import shirates.core.vision.testcode.VisionTest
class Macro1 : VisionTest() {
@Test
@Order(10)
fun macro1() {
scenario {
case(1) {
action {
it.macro("[Network preferences Screen]")
}.expectation {
it.exist("Install certificates")
}
}
}
}
}
Run the test code. You can see a log line on console as follows.
[info] () Registering macro. (macro.MacroObject1)