Irregular Handler (Global Handler)
In smartphone apps, irregular screens are often inserted in the middle of screen transitions.
You may or may not see these screens.
- popup dialog (e.g. Location Permissions, Network Error, Firebase In-App Messaging, ads)
- tutorials to explain how to use features
- notification balloons.
- others
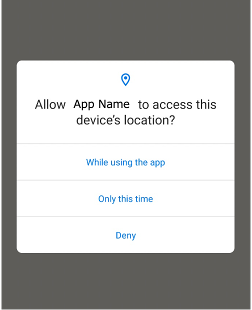
To handle these irregulars, you have to implement conditional branching. That’s very annoying.
AnnoyingEventHandling1.kt
(kotlin/tutorial/inaction/AnnoyingEventHandling1.kt)
@Test
@Order(10)
fun annoyingEventHandling1() {
scenario {
case(1) {
condition {
it.macro("[Some Screen]")
.ifCanSelect("While using the app") {
it.tap()
}
}.action {
it.tap("[Button1]")
.ifCanSelect("While using the app") {
it.tap()
}
}.expectation {
it.screenIs("[Next Screen]")
}
}
}
}
@Test
@Order(20)
fun annoyingEventHandling2() {
scenario {
case(1) {
condition {
it.macro("[Some Screen2]")
.ifCanSelect("While using the app") {
it.tap()
}
}.action {
it.tap("[Button2]")
.ifCanSelect("While using the app") {
it.tap()
}
}.expectation {
it.screenIs("[Next Screen]")
}
}
}
}
irregularHandler
You can centralize irregular handling procedure using irregularHandler.
To apply to all test functions in the TestClass, override setEventHandlers function and set delegate function to context.irregularHandler.
irregularHandler is invoked every time on command execution. This mechanism is very powerful and makes the test code simple.
IrregularHandler1.kt
(kotlin/tutorial/inaction/IrregularHandler1.kt)
@Testrun("testConfig/android/androidSettings/testrun.properties")
class IrregularHandler1 : UITest() {
override fun setEventHandlers(context: TestDriverEventContext) {
context.irregularHandler = {
ifCanSelect("While using the app") {
it.tap()
}
}
}
@Test
@Order(10)
fun irregularHandler1() {
scenario {
case(1) {
condition {
it.macro("[Some Screen]")
}.action {
it.tap("[Button1]")
}.expectation {
it.screenIs("[Next Screen]")
}
}
}
}
}
Note:
- A lot of procedure in irregularHandler may cause performance problem. Consider using On Error Handler or Screen Handler instead.
- Logging is suppressed while executing irregularHandler delegate function by default.
suppressHandler
You can suppress firing irregularHandler by using suppressHandler function.
@Test
@Order(20)
fun suppressHandler_useHandler() {
scenario {
case(1) {
condition {
it.macro("[Some Screen]")
}.action {
/**
* In suppressHandler block,
* calling irregular handler is suppressed
*/
suppressHandler {
it.tap("[Button1]")
}
}.expectation {
it.screenIs("[Next Screen]")
}
}
case(2) {
action {
/**
* In suppressHandler block,
* calling irregular handler is suppressed
*/
suppressHandler {
it.tap("[Button2]")
/**
* In useHandler block,
* calling irregular handler is enabled
* even if it is nested in suppressHandler block
*/
useHandler {
it.tap("[Button3]")
}
}
}
}
}
}
disableHandler(), enableHandler()
You can disable or enable handler by these functions.
@Test
@Order(30)
fun disableHandler_EnableHandler() {
scenario {
case(1) {
condition {
it.macro("[Some Screen]")
}.action {
disableHandler() // Calling irregular handler is disabled.
it.tap("[Button1]")
ifCanSelect("While using the app") {
it.tap()
}
enableHandler() // Calling irregular handler is enabled again.
}.expectation {
it.screenIs("[Next Screen]")
}
}
}
}